
Nitrogen Understanding Global Change
Animals secure their nitrogen (and all other) compounds from plants (or animals that have fed on plants). Figure 17.2.2.1 Nitrogen cycle. Four processes participate in the cycling of nitrogen through the biosphere: (1) nitrogen fixation, (2) decay, (3) nitrification, and (4) denitrification. Microorganisms play major roles in all four of these.

nitrogen fixation Definition, Process, Examples, Types, & Facts
Core Concept Earth Sciences Published: March 12, 2019 What Is the Nitrogen Cycle and Why Is It Key to Life? Authors Miriam R. Aczel Young Reviewers Juliette Claire Abstract Nitrogen, the most abundant element in our atmosphere, is crucial to life. Nitrogen is found in soils and plants, in the water we drink, and in the air we breathe.

Nitrogen Cycle QCE Biology Revision
. Nitrogen exists in the atmosphere as N 2 gas. In nitrogen fixation, bacteria convert N 2 into ammonia, a form of nitrogen usable by plants. When animals eat the plants, they acquire usable nitrogen compounds. Nitrogen is a common limiting nutrient in nature, and agriculture.

What is Nitrogen Fixation The Tree Center™
Good question! There are many different types of nitrogen fixation (most of which are not well studied) — my answer focuses on the system where Rhizobia (a genus of bacteria) associate with a group of plants known as legumes (e.g.s beans, clovers, alfalfa). The Rhizobia are encased in a structure known as a nodule on the roots of legumes. The nodule protects the bacteria and serves as a site.
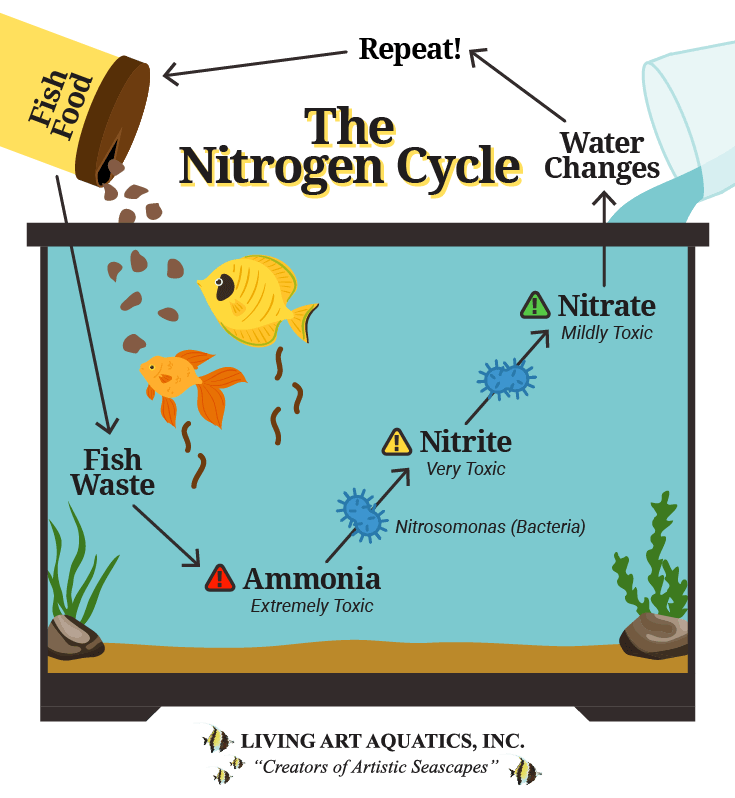
The Nitrogen Cycle Process Living Art Aquatics
The labeled nitrogen cycle diagram is shown below: Steps of Nitrogen Cycle. The stages of nitrogen cycle are explained as follows: Nitrogen Fixation. Atmospheric nitrogen (N 2) is converted into ammonia (NH 3)or ammonium ions (NH4 +) through biological, industrial, or natural processes. Nitrogen-fixing bacteria, such as those in the genera.
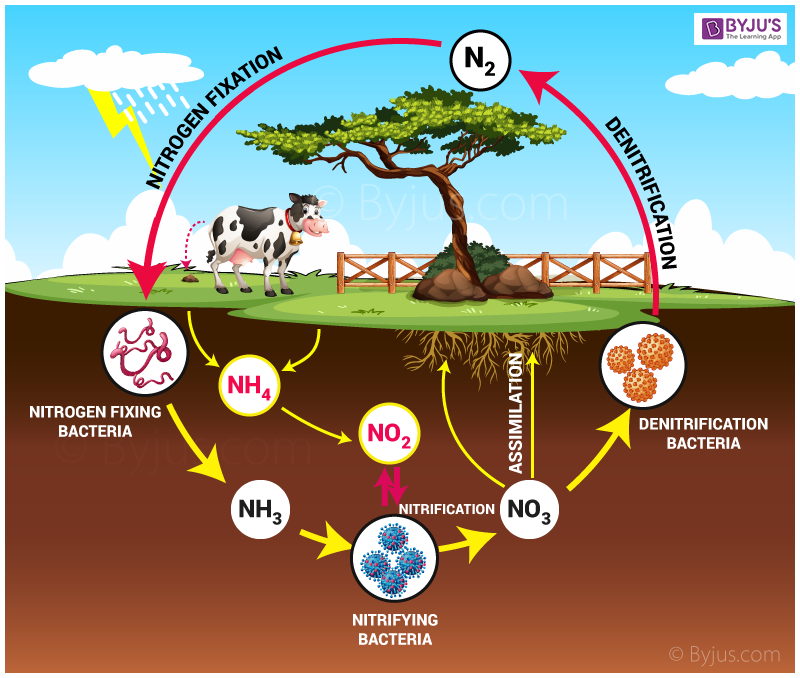
Nitrogen Cycle Introduction, Stages and its Process
The nitrogen cycle is the biogeochemical cycle by which nitrogen is converted into multiple chemical forms as it circulates among atmospheric, terrestrial, and marine ecosystems. The conversion of nitrogen can be carried out through both biological and physical processes.

Why is the Nitrogen Cycle So Important? •
Nitrogen cycle, circulation of nitrogen in various forms through nature. Nitrogen, a component of proteins and nucleic acids, is essential to life on Earth. Although 78 percent of the atmosphere is nitrogen gas, this gas is unusable by most organisms until it is made available by a series of microbial transformations.

How the Nitrogen Cycle Works Britannica
1. Nitrogen-fixation Legume plants such as peas, beans and clover contain nitrogen-fixing bacteria. These bacteria live in swellings in the plant roots called nodules . Nitrogen-fixing.
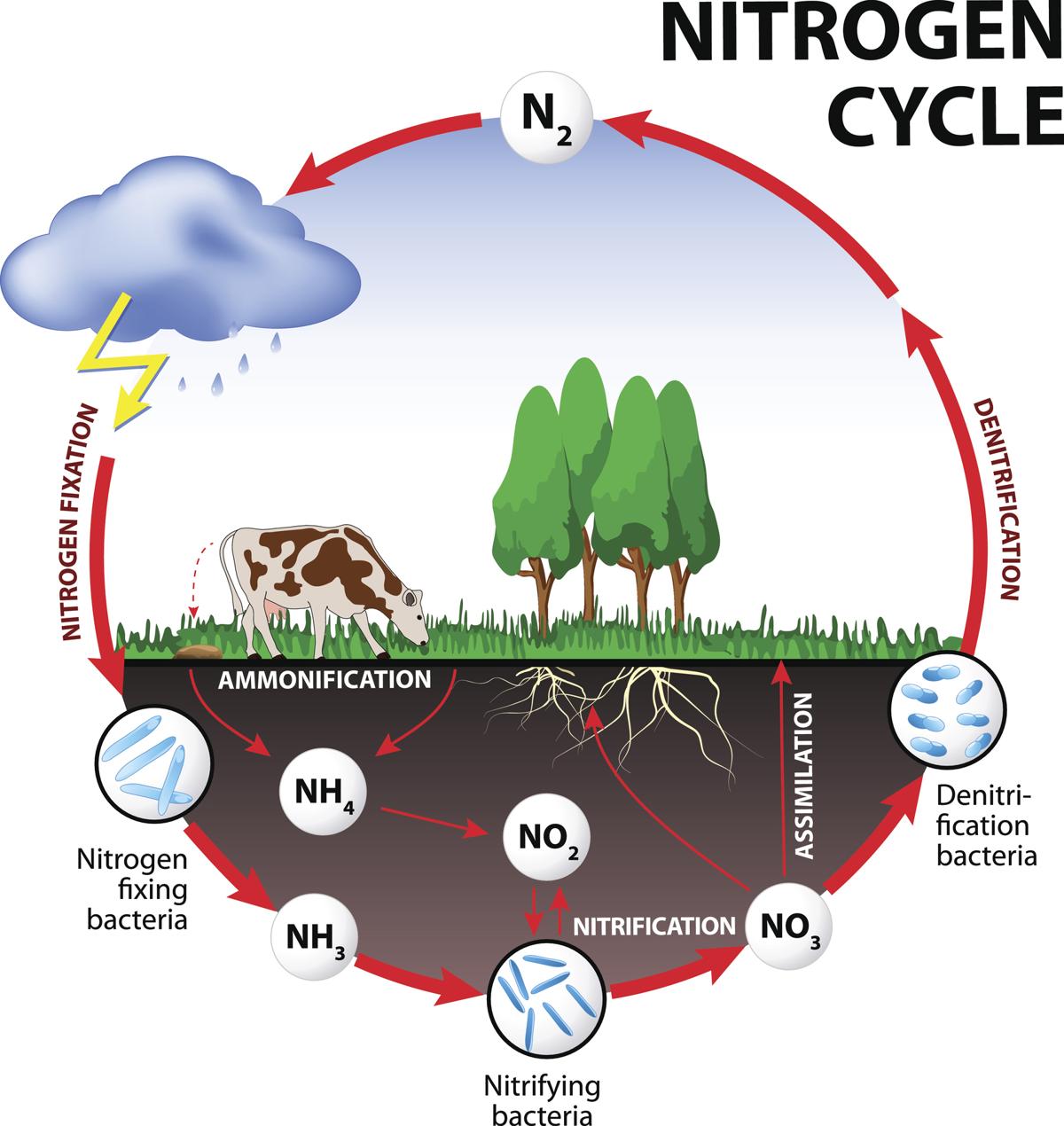
Nitrogen cycle Steps of Nitrogen cycle Online Biology Notes
The nitrogen cycle — Science Learning Hub Article The nitrogen cycle Resource Related topics & concepts Add to collection Nitrogen is the most abundant element in our planet's atmosphere. Approximately 78% of the atmosphere is made up of nitrogen gas (N 2). Topics Concepts Citizen science Teacher PLD Glossary Sign in Email Us

Nitrogen Cycle Facts for Kids (Explained!) Education site
The nitrogen cycle refers to the cycle of nitrogen atoms through the living and non-living systems of Earth. The nitrogen cycle is vital for life on Earth. Through the cycle, atmospheric nitrogen is converted to a form which plants can incorporate into new proteins. Nitrogen Cycle Explained

301 Moved Permanently
The final step of the nitrogen cycle is denitrification wherein nitrates in the soil are broken down and nitrogen is finally released in the atmosphere - completing the nitrogen cycle. Nitrogen is one of the components of many explosives. Nitrogen is colorless, tasteless, and odorless. Around 3% of the human body weight is made up of nitrogen.
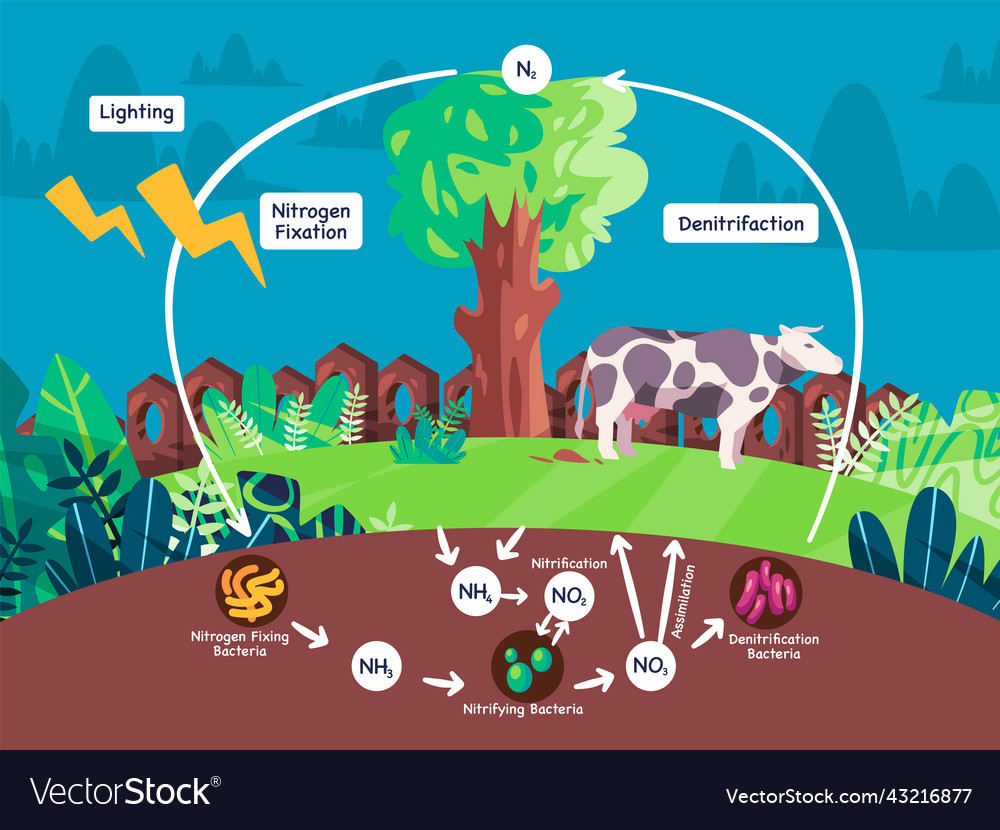
Nitrogen cycle diagram biogeochemical process Vector Image
Understanding Nitrogen Cycle with a Diagram Similar to other biogeochemical cycles, the nitrogen cycle is essential for regulating the concentration of nitrogen in the atmosphere. Read on to know more about this cycle through the diagram given below, which will help you in understanding the sequence of steps involved in this cycle.
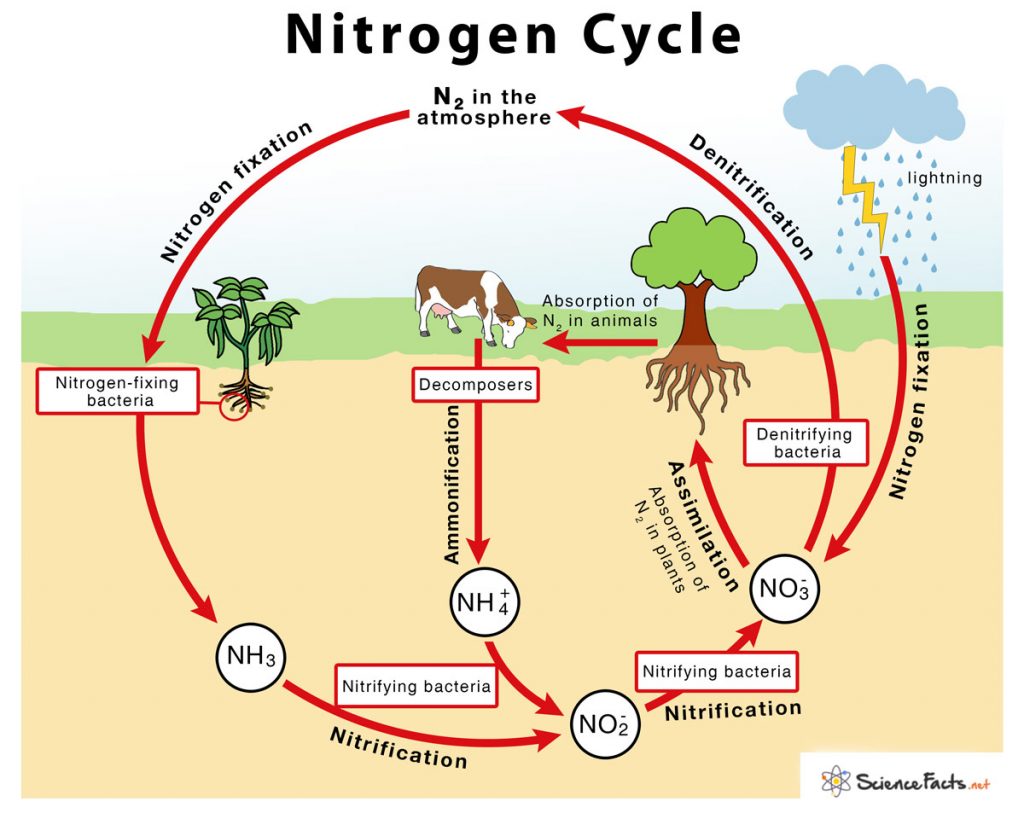
Nitrogen Cycle Definition, Steps, Importance with Diagram
The nitrogen cycle is the cyclic movement of nitrogen in different chemical forms between living organisms and the environment. The steps of the nitrogen cycle are described below. Nitrogen fixation: During this step, atmospheric nitrogen gas is fixed, or converted into a form that can be used by plants and animals.

Tom's Marine Biology A block Diagram of Nitrogen Cycle
Introduction Nitrogen is one of the primary nutrients critical for the survival of all living organisms. It is a necessary component of many biomolecules, including proteins, DNA, and chlorophyll.
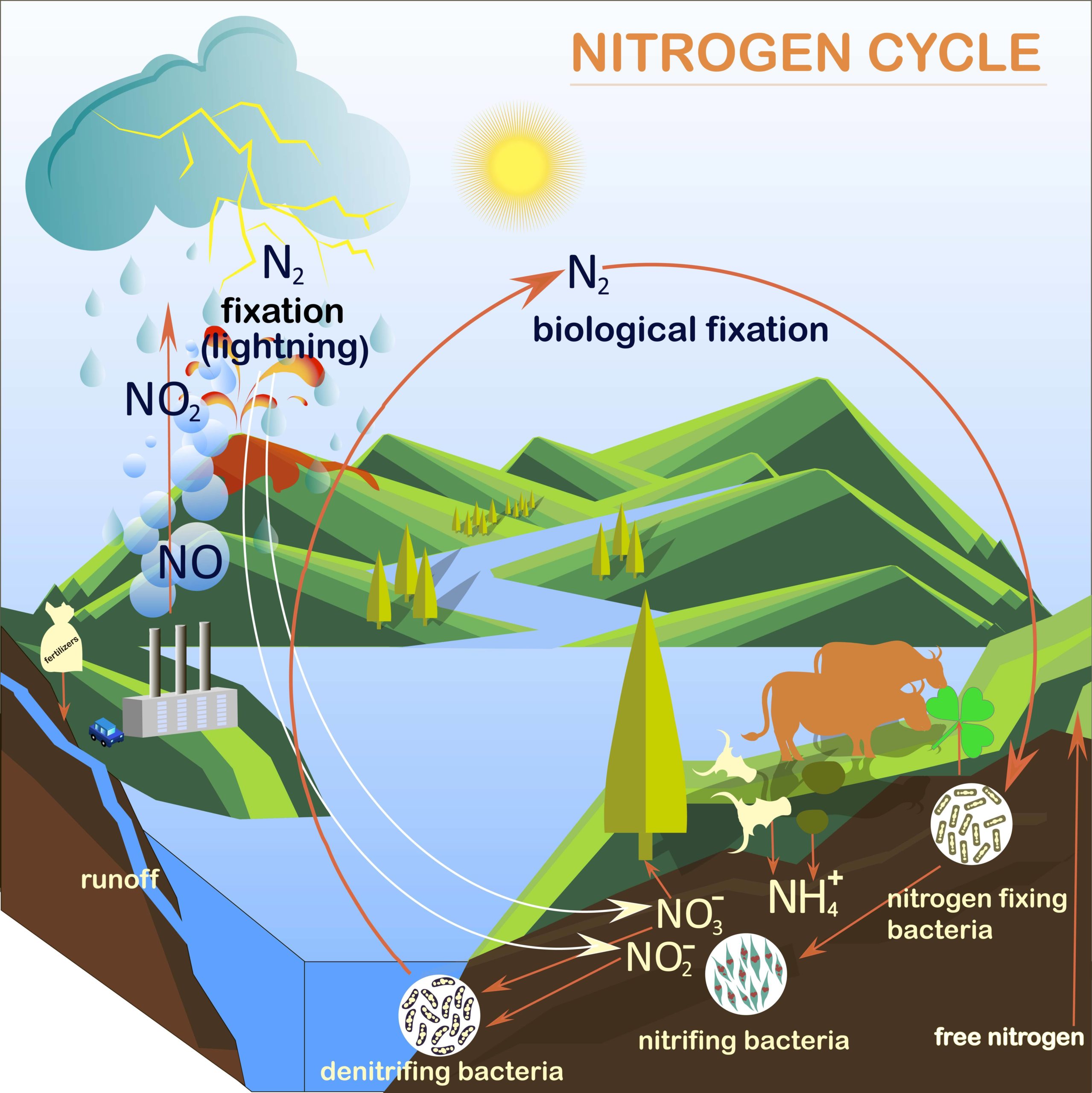
What is the Nitrogen Cycle? Science for Kids
Nitrogen Cycle is a biogeochemical process through which nitrogen is converted into many forms, consecutively passing from the atmosphere to the soil to organism and back into the atmosphere. It involves several processes such as nitrogen fixation, nitrification, denitrification, decay and putrefaction.
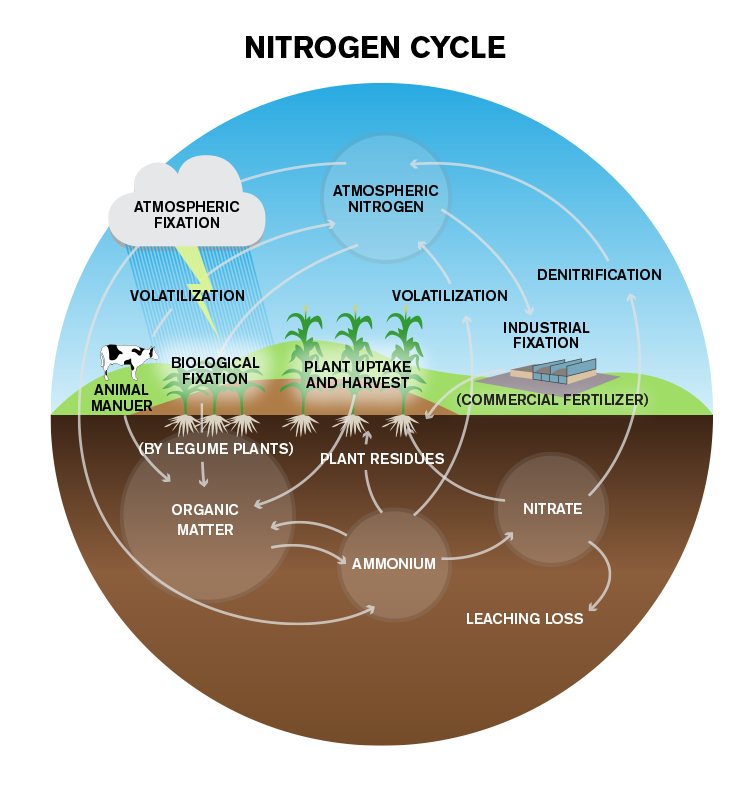
Nitrogen Cycle Steps Process Explanation Diagram
From an ecological perspective, the nitrogen cycle consists of the following stages: (i) Ammonification (ii) Nitrification, (iii) Nitrogen uptake by plants, ADVERTISEMENTS: (iv) Fixation of Nitrogen, and (v) Denitrification Ammonification: